The space economy is no longer the exclusive domain of governments or a select group of traditional players. Today, private enterprises are leading the charge in satellite launches, interplanetary exploration, and commercial space ventures, reshaping this dynamic frontier. Even industries previously unassociated with space are stepping into this arena. A striking example is Toyota’s recent $44 million investment in Interstellar Technologies, a Japanese rocket company. By leveraging its renowned manufacturing expertise, Toyota aims to revolutionize Japan’s fledgling space industry, positioning it to compete with global giants like SpaceX.
This strategic partnership highlights a broader trend: transforming space from a domain riddled with challenges into a thriving sector primed for exponential growth. With the Japanese government actively fostering space innovation and Toyota’s pioneering role, Japan is poised to establish itself as a significant player in the $630 billion global space economy.
Global Growth and India’s Aspirations
The global space economy, valued at $630 billion in 2023, is expected to reach a staggering $1.8 trillion by 2035. This growth is largely fueled by private sector leaders like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic, which are advancing reusable rockets, satellite constellations, and commercial spaceflight.
India, with its innovative and cost-efficient missions, holds immense potential in this evolving landscape. While its space economy was valued at $8.4 billion in 2023, India aims to expand this to $44 billion by 2033, capturing a 7-8% share of the global market and generating $11 billion in exports. Projects like ISRO’s Mars Orbiter and Gaganyaan human spaceflight, coupled with over 250 space-tech startups, underscore India’s ability to deliver transformative solutions. Public-private partnerships are enabling advancements in satellite manufacturing and space applications, fostering greater global digital connectivity and bridging developmental gaps. (PIB), (McKinsey)
Transformative Applications of Space Technology
The space economy’s most profound impact lies in its practical applications across critical sectors, driving progress and innovation.
Advancing Agriculture
Precision farming, powered by satellite technology, is revolutionizing agriculture. Real-time monitoring of crop health, soil moisture, and weather conditions allows farmers to detect pests and diseases early, potentially reducing crop losses by 20-40%. Additionally, climate-monitoring satellites help predict weather patterns and mitigate drought risks, safeguarding millions of livelihoods globally. (WeForum)
Strengthening National Security
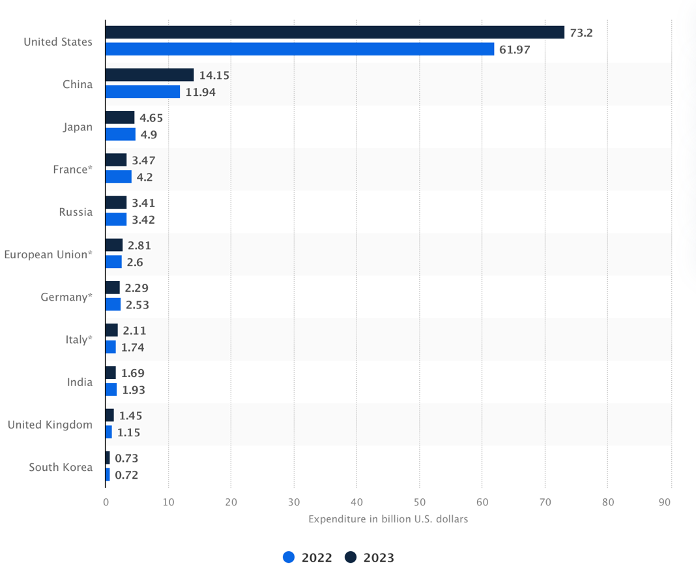
Satellites are indispensable for modern defence, offering geospatial intelligence and situational awareness. Despite the United States’ $73.2 billion space program budget in 2023, India’s comparatively modest $1.69 billion allocation underscores the need for increased investment in strategic capabilities. (Statista)
Government expenditure on space programs by major countries in 2022 and 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Enhancing Disaster Management
Satellite technology plays a critical role in disaster response. For instance, during the 2020 Beirut explosion, satellite imagery facilitated rapid damage assessment, improving response efficiency and showcasing the life-saving potential of space-driven solutions. (UNOSAT)
Optimising Logistics
Advances in satellite-enabled GPS systems are transforming supply chain management. Real-time tracking has reduced delivery complaints by 30% and decreased fuel consumption by 10% per trip. The market for satellite-enabled tracking systems is projected to grow from $15.2 billion in 2020 to $44.1 billion by 2025. (Frayto)
Catalysing Growth and Job Creation
India’s burgeoning space economy is a driver of economic growth and job creation. Organizations like ISRO and private startups generate opportunities for engineers, scientists, and mission controllers, while advancements in robotics, AI, and materials sciences ripple across related industries. Innovations in spacecraft materials are influencing consumer electronics and automotive technologies, demonstrating the sector’s far-reaching impact.
Space Tourism and Public-Private Collaborations
The global space tourism market, valued at $888.3 million in 2023, is projected to soar to $10 billion by 2030, fueled by the rise of sub-orbital and orbital flights. At the heart of this growth lies the transformative role of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs), which are revolutionizing space exploration by drastically improving cost efficiency. Programs like NASA’s Commercial Crew initiative, in collaboration with SpaceX and Boeing, exemplify this shift by significantly reducing the cost of space missions compared to traditional government-led efforts. For instance, while the Apollo Program cost $25.8 billion (approximately $257 billion today), SpaceX’s Crew Dragon program has set new industry standards by leveraging reusable rocket technology. This innovation not only slashes costs but also enhances safety and reliability, demonstrating how PPPs are paving the way for a more accessible and economically sustainable space economy. (Horizon), (Forbes)
Global space tourism market, 2017-2030 (US$M)


Conclusion
In wrapping up, the space economy is entering an exciting new chapter, driven by the ingenuity of private companies, forward-thinking government policies, and groundbreaking technologies. From boosting agricultural productivity and optimizing logistics to strengthening disaster response and national security, the impact of space is rippling across every facet of our lives. With nations like Japan and India stepping up their game, the potential for innovation and economic growth in this sector has never been greater. As investments grow and collaborations deepen, the once-distant dream of making space accessible to all is becoming a reality. The space economy isn’t just about exploring new frontiers—it’s about transforming the way we live, work, and connect here on Earth. The sky, quite literally, is no longer the limit.
