3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is revolutionising healthcare by enabling the production of personalised prosthetics, implants, surgical tools, and even bio-printed tissues. The industry in the Indian market especially holds great untapped potential, with opportunities for growth as action plans, government policies, and regulations continue to evolve.
This article delves into the potential of 3D printing in healthcare, with a focus on personalised prosthetics, custom implants, bio-printing, and its integration into hospital operations. Additionally, it explores market trends, economic implications, and the future trajectory of this technology.
REIMAGINING MEDICINE WITH TECH
The healthcare industry is continuously evolving with the integration of ground-breaking technologies. Among these, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative force, capable of reshaping medical manufacturing processes. Known for its ability to create complex, customised structures, 3D printing is increasingly being adopted in hospitals and medical research facilities worldwide. In India, the healthcare sector is rapidly embracing 3D printing, particularly for orthopedic and dental applications, with the use of metal 3D printed parts.
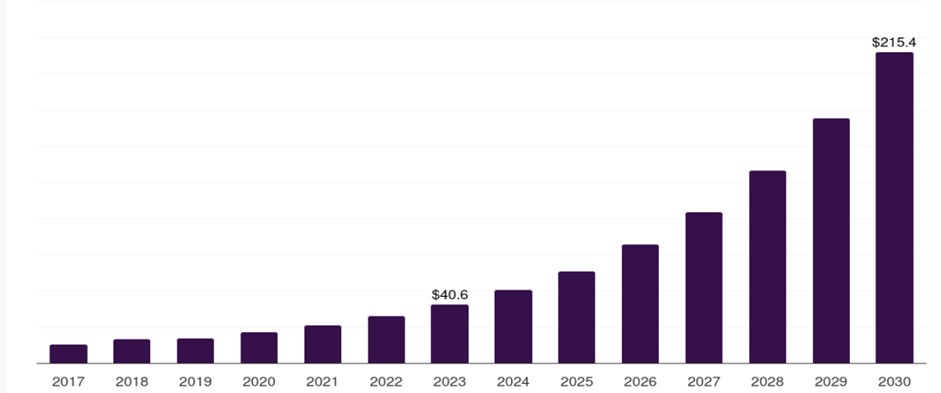
Forecast of Indian 3D printing market size from year 2017 to year 2030 in US$ millions
ADVANCEMENTS IN PERSONALIZED HEALTHCARE
- Personalised Prosthetics: Cost-Effective Precision
Traditional prosthetics are not only expensive but also require extensive customization processes involving multiple fittings. 3D printing offers a faster, cost-effective alternative by enabling the creation of prosthetics tailored to an individual’s anatomy using precise 3D scans. This approach significantly enhances comfort, functionality, and patient satisfaction.
- The Growing Prosthetics Market: Challenges and Opportunities
The global prosthetics market is on a steady growth trajectory, with a projected CAGR of 5.7% over the next seven years. By 2025, this market is expected to reach an estimated value of $2.8 billion. Despite this promising expansion, the high costs associated with prosthetics remain a significant barrier for many individuals in need.
Researchers at IIT Guwahati have developed an affordable prosthetic limb tailored to Indian conditions. Designed to navigate uneven terrain, it also supports traditional postures like cross-legged sitting and deep squatting. Prosthetics, though affordable elsewhere, often remain costly in comparison to local incomes, limiting access for many. Ensuring affordability and accessibility is vital to making advancements in prosthetic technology widely beneficial.
- Custom Implants: Optimised Integration and Recovery
3D printing has revolutionised the manufacturing of medical implants, such as cranial plates, joint replacements, and dental fixtures. Unlike standardised implants, which often require manual adjustments during surgery, 3D-printed implants can be customised to fit a patient’s anatomy precisely. This reduces surgical risks, enhances recovery outcomes, and minimises complications.
A study involving 41 craniomaxillofacial reconstructions demonstrated significant benefits of using 3D-printed patient-specific implants. These implants ensured reduced surgical time, faster recovery, and fewer complications such as stress fractures or implant fatigue.
BIOPRINTING: A FRONTIER IN MEDICAL INNOVATION
- Addressing Organ Shortages
Bioprinting, a specialised form of 3D printing, involves layering living cells to create tissue-like structures. It holds immense promise for addressing the global shortage of organs available for transplantation. In the U.S. alone, over 1,03,000 people await organ transplants, with 17 individuals dying daily due to limited availability. Bioprinting could offer a lifeline by enabling the creation of implantable human tissues and organs.
However, challenges remain, particularly in ensuring adequate oxygen and nutrient delivery to lab-grown tissues. Indian medical experts are making significant progress in exploring the engineering aspects to make tissue engineering a reality. To mention, Pandorum Technologies, based in Bengaluru, is working on bioengineered ‘liquid corneas’ capable of regenerating human corneas. Overcoming obstacles could therefore unlock the potential for bio-printing to revolutionise regenerative medicine and organ transplantation.
- Applications in Pharmaceutical Research
Bioprinting is also poised to transform drug testing and development. By creating accurate human tissue models, researchers can test drugs in a more ethical and efficient manner, reducing reliance on animal testing and accelerating the development of life-saving medications.
ON-SITE 3D PRINTING IN HOSPITALS
- Customised Medical Devices
Many hospitals are adopting on-site 3D printing capabilities to produce patient-specific devices and tools on demand such as surgical guides, splints, orthotics, and even prosthetics. This eliminates delays associated with outsourcing, making it particularly valuable in emergencies.
Hospitals also employ 3D printing to produce anatomical models for diagnosis and surgical planning. These models are particularly helpful for intricate treatments involving newborns and toddlers, whose distinct anatomy frequently calls for specialised methods.
- Innovations in Materials and Biodegradable Solutions
High-performance polymers will be used in future 3D printing projects to produce advanced medical devices. Compared to more conventional techniques like injection moulding, rapid prototyping allows for iterative design processes that are quicker and more economical.
Additionally, experts are exploring biodegradable medical devices, like stents, which dissolve after serving their purpose and do not require surgical removal.
3D printing is making waves in healthcare, by providing:
- Enhanced Accessibility: Mobile 3D printing units could empower rural and under-resourced hospitals to locally produce essential medical devices, reducing dependency on distant suppliers.
- Efficient Inventory Management: By enabling hospitals to print devices on demand, this technology can significantly reduce inventory requirements and minimise waste.
As 3D printing continues to evolve, its economic and practical benefits across industries promise to reshape traditional workflows, making them more efficient, sustainable, and accessible. Bengaluru-based start-up Avay Biosciences, a pioneer in manufacturing 3D bioprinters, produces four widely used bioprinting polymers: alginate, gelatin methacryloyl, agarose, and pluronics. The company is also working on developing cost-effective collagen-based biomaterials tailored for the Indian market.
SEGMENTS OF 3D PRINTING INDUSTRY
The global healthcare 3D printing market was valued at USD 8.52 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.5% from 2024 to 2030. Key factors, such as public-private funding, growing demand for patient-specific implants, and high production accuracy, further contribute to the market’s expansion. The application scope includes products such as medical implants, prosthetics, wearable devices, tissue engineering, dental solutions, and more. The dental segment, accounting for 36.7% of the revenue share in 2023, has revolutionised dentistry by being economical and enabling the design of personalised prosthetics. Tissue engineering, projected to grow at a CAGR of 15.0%, benefits from the ability to create customised scaffolds that support cell growth and tissue regeneration.
On the technological front, advancements like Stereolithography, Deposition Modelling, Electron Beam Melting, Laser Sintering, Jetting Technology, and Laminated Object Manufacturing are shaping the field. Laser sintering led the market with a 30.1% revenue share in 2023, owing to its capability to produce highly customised, precisely engineered implants using biocompatible materials. Deposition modelling, with an anticipated CAGR of 20.8%, is transforming personalised medicine by enabling the creation of customised dosage forms with controlled drug release rates.
Materials, especially polymers, are dominating at 54.6% in 2023 due to their flexibility, biocompatibility, and ability to engineer minimally invasive devices. Biological cells, growing at a CAGR of 20.3%, are instrumental in creating complex tissue structures and enhancing therapeutic effects. Materials currently utilised in 3D printing span a variety of categories, including metals and alloys like steel and titanium, as well as polymers such as nylon, glass-filled polyamide, epoxy resins, photopolymers, plastics, and even biological cells.
EMBRACING THE POSSIBILITIES
India’s 3D printing market has experienced rapid growth in recent years. Valued at $92.34 million in 2022, the market is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20.33% by 2028.
3D printing is undeniably revolutionising the healthcare industry by bridging the gap between innovation and accessibility. From personalised prosthetics and custom implants to bioprinting and on-demand production in hospitals, its applications are reshaping medical manufacturing and patient care. The technology’s ability to address pressing challenges, such as organ shortages, cost inefficiencies, and the need for personalised treatments, underscores its transformative potential. As market trends point toward exponential growth fueled by technological advancements and increasing adoption, 3D printing is set to become a cornerstone of modern healthcare. However, addressing challenges such as regulatory hurdles, material limitations, and scalability will be crucial for unlocking its full potential. With its promise to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve outcomes, 3D printing stands poised to redefine the future of medical manufacturing and elevate the standard of care worldwide.